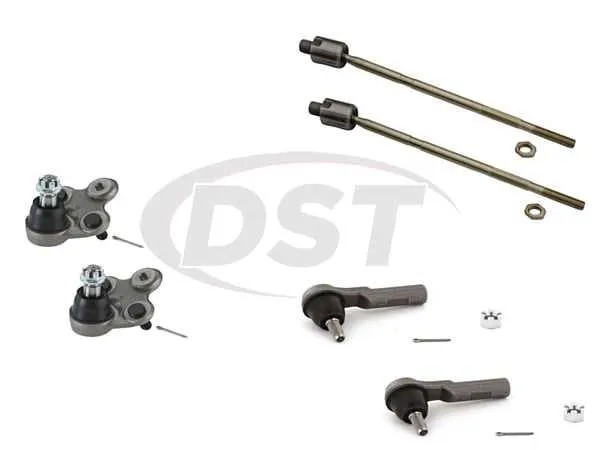

If you’re troubleshooting or upgrading the front axle assembly of your vehicle, understanding its layout is essential for accurate repairs and replacements. Begin by identifying the key components, such as the lower control arm, strut assembly, and stabilizer bar, as well as their attachment points. Analyzing the connections between the subframe and the wheel assembly will help you spot any potential issues like wear or misalignment.
The first step is to examine the shock absorber and its integration with the steering knuckle. This connection is crucial for maintaining proper handling and ride comfort. Pay close attention to the bushings and the upper mount, as they often wear down due to constant stress. It’s also important to assess the integrity of the steering rack and its linkages, which play a pivotal role in vehicle response.
For optimal performance, make sure all fasteners are torqued to the manufacturer’s specifications. Any deviation from the correct settings can result in instability or uneven tire wear. If replacing any components, choose high-quality parts that meet OEM standards. Additionally, ensure that all rubber seals are intact to prevent dirt and moisture from affecting the components.
Detailed Breakdown of the Vehicle’s Suspension System Components
For precise diagnostics and repair, it is crucial to understand the configuration of the primary elements that support the vehicle’s front axle. Begin by identifying key components such as the lower control arm, upper strut mount, coil spring, and sway bar links. These elements work in unison to maintain alignment and stability while driving.
Upper strut mount connects directly to the vehicle frame and absorbs forces from the steering wheel while maintaining proper alignment of the shock absorber. It’s essential to inspect this part for wear and noise, which could indicate a failure of the bearing or mounting point.
The lower control arm plays a critical role in keeping the wheel in position relative to the vehicle body. It should be regularly checked for any bending or cracking, particularly in areas exposed to heavy stress during turns or sudden stops. Ensure the bushings are intact to prevent misalignment and improper handling.
Coil springs are designed to support the vehicle’s weight and absorb road shock. Over time, they can sag, affecting ride quality. A visual inspection for any signs of corrosion or breaks is recommended.
The sway bar links help reduce body roll during cornering by connecting the sway bar to the suspension. Inspect these links for any looseness or damage to ensure optimal handling performance. If the bar is not secured correctly, you might experience more pronounced swaying when navigating turns.
To accurately service these components, refer to an assembly chart showing all mounting points and connections. This will ensure that each piece is replaced or adjusted correctly to restore the intended driving dynamics.
Understanding the Key Components of the 2007 Honda CR-V Front Suspension System
The front suspension system of your vehicle plays a crucial role in ensuring proper handling, stability, and ride comfort. Below is a breakdown of the critical components and their functions:
- Upper Control Arm: This component connects the wheel hub to the vehicle’s frame, allowing controlled vertical movement. It ensures that the wheel stays aligned during turning or when the vehicle encounters uneven surfaces.
- Lower Control Arm: Acting as a counterpart to the upper control arm, the lower arm maintains proper wheel alignment while absorbing road irregularities. It is usually attached to the steering knuckle and provides support during braking or acceleration.
- Strut Assembly: Positioned between the vehicle’s body and the wheels, the strut serves as both a shock absorber and a structural component. It helps dampen the impact from rough roads, contributing to a smooth driving experience.
- Coil Spring: Typically located around the strut, coil springs support the weight of the vehicle. They compress and expand, ensuring that the vehicle remains level and absorbs shocks from the road surface.
- Steering Knuckle: This piece connects the wheel hub to the suspension and steering components, allowing the wheels to pivot during steering. It directly impacts the vehicle’s handling and response to steering inputs.
- Ball Joints: Ball joints allow for the free movement of the suspension components while maintaining a stable connection between the control arms and the steering knuckle. They facilitate smooth rotation during steering and suspension travel.
- Sway Bar (Anti-roll Bar): This part stabilizes the vehicle during turns by reducing body roll. It connects the left and right suspension components and ensures that the car maintains a balanced position on the road.
- Wheel Hub: The wheel hub serves as the interface between the wheel and the suspension, enabling the wheel to rotate freely while maintaining secure attachment to the vehicle.
Regular maintenance of these components is vital for vehicle safety and performance. Failure to address worn-out parts can lead to handling issues, reduced comfort, and potential damage to other suspension components.
Step-by-Step Guide to Interpreting the Suspension Components Diagram
Begin by identifying the key sections in the diagram: the upper and lower control arms, the strut assembly, and the wheel hub. Each part is numbered for easy reference, with lines showing how components connect to each other.
Step 1: Focus on the control arms, which are typically positioned on both sides of the frame. These parts form the primary link between the wheel and the vehicle body. Check for any wear signs such as cracks or bends in the metal.
Step 2: Next, locate the strut assembly, often central to the diagram. This component integrates the shock absorber and the coil spring. It’s crucial to identify the mounting points where the strut connects to the control arms and the vehicle chassis. Ensure the bushings are intact, as these provide flexibility and reduce noise.
Step 3: Move on to the wheel hub, which houses the wheel bearings. Pay attention to the axle and the spindle connection. Misalignment or wear here can lead to uneven tire wear or handling issues.
Step 4: Examine the tie rods and ball joints, which facilitate steering movement. Proper lubrication and tightness are vital for responsive handling and reducing vibration.
Step 5: Identify the anti-roll bar, which connects the left and right suspension components. This part helps stabilize the vehicle, reducing body roll during turns. Check for secure mounting and the absence of cracks.
By following these steps, you can understand the function and positioning of each piece in the assembly, ensuring maintenance and repairs are performed correctly.
Common Issues with the Front Suspension and How to Diagnose Them
Excessive Steering Play: If you notice more play in the steering wheel than usual, it could be a sign of worn-out tie rod ends or steering rack issues. To diagnose, park the vehicle on a flat surface, then turn the steering wheel left and right. If there’s noticeable movement before the tires respond, inspect the tie rods and steering rack for signs of wear or damage.
Unusual Noises While Driving: Clunking or knocking sounds when driving over bumps often point to worn-out control arm bushings or ball joints. To check, jack up the vehicle, grasp the wheel at 12 and 6 o’clock positions, and try moving the wheel. Any noticeable play indicates worn components.
Pulling to One Side: If the vehicle pulls to one side while driving, it can indicate misalignment or a damaged strut. Begin by checking tire pressures to rule out uneven inflation. Then, perform a wheel alignment check. If the alignment is correct, inspect the shock absorbers for leaks or wear.
Vibration at High Speeds: Vibration when driving at highway speeds could be due to worn-out wheel bearings or unbalanced tires. To check, jack up the vehicle and spin the wheels by hand. Listen for any rough noises or feel for any resistance, which could indicate bearing wear. Unbalanced tires can also be identified through a visual inspection for abnormal wear patterns.
Uneven Tire Wear: Uneven tire wear often points to alignment issues or problems with struts and shocks. Inspect the tread pattern across all tires. If the tread is more worn on the inside or outside, misalignment is likely the cause. If the wear is more even but still irregular, consider checking the shock absorbers for signs of leakage.
Leaking Fluid: Fluid leakage around the shock absorbers or struts is a clear indication of internal damage. Check for any visible fluid around the shocks and struts, which may be damp or streaked. If fluid is present, replacement of the strut assembly is necessary to restore proper function.