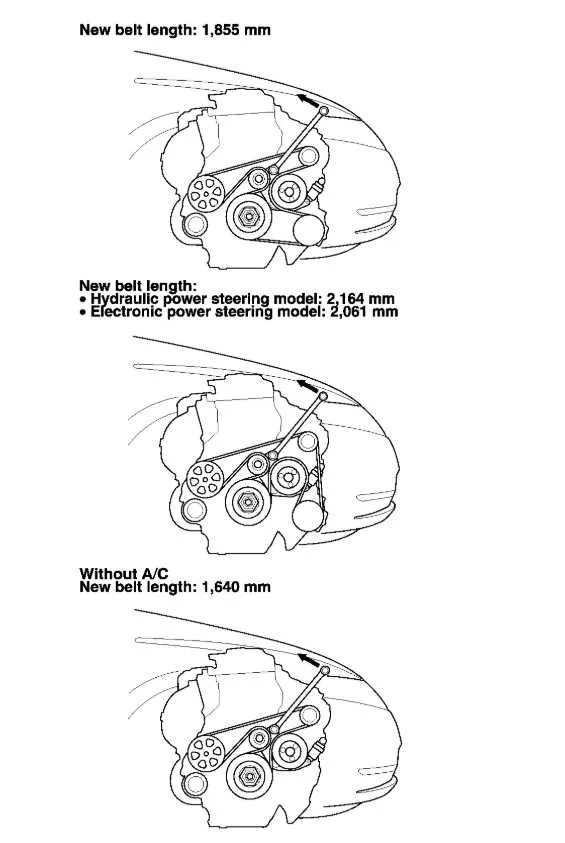
To ensure proper functionality and avoid costly repairs, it is crucial to follow the exact routing of the engine’s drive components. For vehicles equipped with the specified engine model, the layout of the auxiliary drive system is vital for maintaining smooth operation. This includes routing for alternator, air conditioning compressor, power steering, and water pump systems.
The optimal sequence begins at the crankshaft pulley, with the belt wrapping around key components in a precise order to maintain the correct tension and power flow. Incorrect routing can cause strain on engine components, leading to premature wear and inefficient performance.
Consult the service manual for the exact component locations, as the arrangement may vary based on the specific engine variant. Accurate installation is paramount to avoid slippage, misalignment, or failure, ensuring that all related systems function without disruption.
Always verify the condition of the drive elements before reassembly, checking for signs of fraying or damage that could compromise the system’s integrity.
Serpentine System Layout and Tensioning Guide
For optimal engine performance, always refer to the correct routing of the serpentine mechanism. The routing guide indicates how the main engine pulley, alternator, AC compressor, and power steering pump are interconnected. The drive components must align properly to ensure that the system runs smoothly, avoiding slippage or over-tensioning. Use a suitable tool to adjust the tensioner and confirm that the tension is within the manufacturer’s specified range.
When replacing the drive system, pay close attention to the direction of rotation and ensure that the pulley grooves align with the belt. Misalignment can lead to excessive wear and failure of the system components. Follow the recommended tensioning procedure, as incorrect tension could either cause premature belt wear or affect the performance of accessories connected to the system.
For quick troubleshooting, examine the belt for cracks, frays, or glazing. Excessive noise during operation might also indicate misalignment or inadequate tension. Regular inspection of these components is crucial to avoid more costly repairs in the future.
How to Identify the Serpentine Routing on a 2012 Honda Civic
Locate the engine’s accessory components like the alternator, power steering pump, and air conditioning compressor. These are connected by a single continuous loop that drives all these parts. Start by finding the tensioner pulley, typically located near the top of the engine, which is responsible for maintaining proper tension on the loop.
Next, identify the crankshaft pulley, often located at the bottom of the engine. This is the primary drive source for the continuous loop. From here, trace the loop as it moves in a clockwise or counterclockwise direction, depending on the engine orientation. Be sure to examine the path of the loop around each pulley, making sure that it passes through the tensioner first and is routed over the alternator and other key components.
If you need help visualizing the exact routing pattern, refer to the underhood decal or consult the factory service manual for a detailed illustration of the precise path. The factory manual will provide you with clear instructions for re-routing or replacing the continuous loop in case of damage or wear.
Finally, always inspect the loop for wear signs, such as cracking, fraying, or glazing. Ensure that the tension is correct to avoid slipping or premature wear on the pulleys. Use a proper tool to release tension and remove the loop if needed, following the routing as indicated by the vehicle’s manual.
Common Issues with the 2012 Honda Civic Belt System
Premature Wear on Serpentine System: One of the most frequent problems with the serpentine system involves premature wear. This often occurs due to improper tension or misalignment. Over time, wear and tear can cause cracks and fraying, leading to failure if not addressed. It’s crucial to inspect the system regularly for visible damage and listen for any unusual noises, such as squealing or chirping.
Incorrect Tensioning: A misadjusted tensioner can result in either excessive slack or too much pressure on the pulleys. Both conditions accelerate wear and may lead to premature failure of the entire setup. If the tension is too high, it puts unnecessary stress on the components, while too little tension can cause slipping and lead to ineffective power transmission.
Damaged or Faulty Pulleys: Pulley issues often arise when the bearings wear out or become clogged with dirt and grime. When the bearings fail, the pulleys can become misaligned, causing further strain on the system. It’s advisable to check each pulley for smooth rotation and proper alignment, as damaged ones can cause excessive noise and may even lead to belt slippage.
Overheating: Overheating can affect both the belts and pulleys. High engine temperatures or malfunctioning cooling systems often contribute to this issue. Persistent heat can dry out rubber belts, causing cracking or stretching. Ensuring the engine cooling system is functioning properly will mitigate the risk of overheating and prolong the life of the serpentine assembly.
Contamination from Fluids: Fluids such as oil, coolant, or power steering fluid leaking onto the serpentine system can deteriorate the rubber material. Once exposed, the belt becomes more prone to cracking and slipping. If leakage is detected, it’s essential to resolve the source of the fluid leak immediately to prevent damage.
Noise and Vibration: Unusual noises or vibrations can indicate a problem with the tensioner, pulleys, or the belt itself. If you hear squealing, it could be a sign that the belt is slipping due to insufficient tension or misalignment. A wobbling sound may indicate a failing pulley or damaged tensioner.
Step-by-Step Guide to Replacing the Drivebelt on a Honda Civic
Replacing the drivebelt is essential to prevent engine performance issues. Follow these steps for a smooth replacement process.
- Prepare Tools and Parts: Gather the following items: new drivebelt, socket set, belt tensioner tool, screwdriver, and a pry bar.
- Locate the Drivebelt: Open the hood and identify the location of the engine drive system. You’ll see the belt running through various pulleys.
- Remove the Old Belt: Use the belt tensioner tool to relieve tension on the belt. Once loosened, carefully slide the belt off the pulleys.
- Check Components: Inspect pulleys, tensioners, and the alternator for wear. Replace any worn-out parts before installing the new belt.
- Install the New Belt: Follow the route outlined in the vehicle manual to thread the new drivebelt. Make sure it sits properly in each pulley groove.
- Apply Tension: Use the belt tensioner tool to adjust the tension of the belt. Ensure it is neither too loose nor too tight.
- Test the Installation: Start the engine and observe the operation of the new belt. Listen for any unusual noises or vibrations.
- Final Inspection: Double-check that the belt is seated correctly and that there are no obstructions or misalignments.
Once completed, your car should be running smoothly with the new drivebelt in place. Always verify the tension periodically to avoid premature wear.