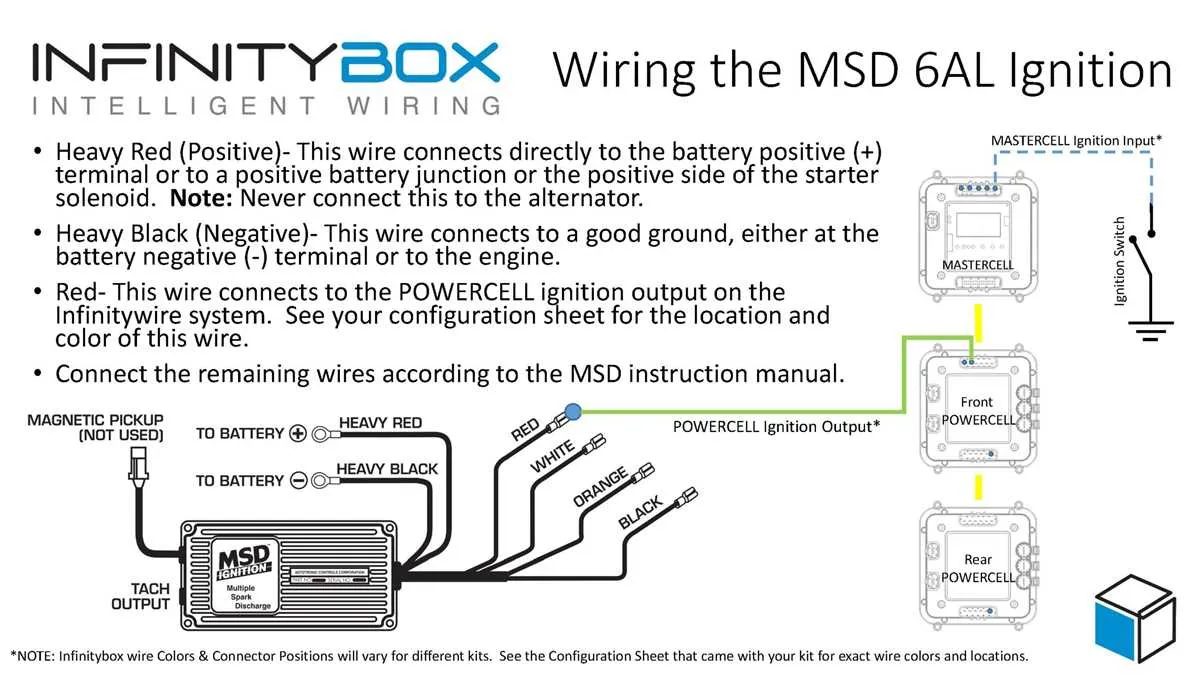
When upgrading to a high-performance ignition system, ensure that you connect each component properly to achieve optimal engine performance. Accurate wiring of the ignition control unit is critical for reliability and precise timing adjustments. Start by verifying the correct placement of power and ground connections to avoid system failures.
Begin with the power supply: The power lead should be connected directly to the battery, with a suitable fuse in place for safety. A poor connection or underpowered wire can result in erratic ignition or even complete system failure.
Next, focus on the signal wire: This wire must be linked to the vehicle’s existing ignition coil or distributor, depending on your setup. Be sure to use wires with sufficient gauge to handle the current load without causing voltage drops. Running the signal wire through protective sleeves will prevent damage from heat or abrasion.
Finally, double-check all connections: Make sure each terminal is securely fastened and insulated. Any loose or exposed wires can lead to misfires, erratic engine behavior, or even ignition system damage. After confirming the setup, test the system before starting the engine to ensure everything is functioning smoothly.
Chevy MSD Wiring Diagram: A Practical Guide
Start by ensuring a secure connection to the ignition system. The power source should be connected to the terminal marked “12V.” Always use a dedicated wire to avoid interference from other components. This ensures a stable voltage supply, crucial for the ignition module’s operation.
Primary Connections: The red wire should be attached to the positive terminal of the battery, while the black wire needs to be grounded to the chassis or engine block. This minimizes the risk of electrical interference, ensuring proper functionality of the ignition system.
Coil Connection: The next step involves connecting the coil to the ignition box. This typically involves attaching the coil’s negative terminal to the unit’s output terminal. Ensure the connection is tight to avoid misfires caused by loose connections.
Trigger Circuit: For optimal performance, connect the trigger circuit from the distributor or control module. This input signal regulates the timing of the ignition system. Proper installation ensures accurate timing and prevents engine knocking.
Check the wiring for any signs of wear or corrosion. Faulty wiring can lead to power loss and system failure. If you detect any issues, replace the wires with high-quality, heat-resistant alternatives to ensure long-term reliability.
Final Test: After completing all connections, perform a system test. Turn the ignition to the “on” position, and use a multimeter to verify voltage and continuity. If everything reads correctly, the system is ready for operation.
How to Connect Ignition System to GM Engine
To properly integrate the ignition control system with your GM engine, follow these steps:
- Locate the Coil Connection: Identify the coil wire that connects to the ignition module. This will be used for the primary signal input to the new control unit.
- Grounding the System: Ensure that all components of the ignition control unit are grounded securely to prevent signal interference. A clean and solid ground is crucial for stable performance.
- Ignition Timing Setup: Adjust the timing of your ignition control box according to the manufacturer’s specifications. This ensures optimal spark delivery to the cylinders.
- Connecting the Distributor: If using a distributor, make sure the timing is synchronized with the control unit. A digital control module may replace the mechanical distributor system entirely.
- Power Supply Connections: The ignition system requires consistent power. Ensure proper connection to the battery or power source, including a fuse for safety. Typically, 12V is required for most setups.
- Signal Wires: Ensure all signal wires from the control module are routed correctly to the engine’s trigger points (e.g., crank position sensor or cam sensor) to detect the engine’s rotation.
- Testing: After making all connections, power on the system and use a timing light to verify spark timing accuracy. Fine-tune if necessary to ensure efficient engine operation.
Always double-check wiring connections and verify component compatibility before finalizing the setup. A clean and efficient installation ensures better engine performance and longevity.
Identifying Common Electrical Issues in Performance Ignition Systems
When installing a performance ignition system, check for proper ground connections. Poor grounding can lead to misfires or inconsistent engine performance. Ensure the ground wire is securely fastened to both the vehicle chassis and the ignition unit. A loose or corroded ground can introduce voltage fluctuations, causing erratic behavior in the ignition timing.
Next, verify that all connections to the power supply are solid and free from corrosion. Corrosion on connectors can significantly reduce the system’s efficiency, leading to weak spark and difficult starting. Use dielectric grease on terminals to prevent moisture buildup and oxidation over time.
Make sure the signal wire from the control box to the ignition coil is routed properly. Interference from other nearby cables can cause signal distortion, resulting in ignition failures or inconsistent spark timing. Keep the signal wire away from high-current cables, especially those supplying power to the fuel pump or starter motor.
Inspect the quality of the ignition coil itself. A faulty coil can cause similar symptoms to a wiring issue. Test the coil for continuity and resistance to confirm its integrity before concluding that the problem lies in the electrical connections.
If you experience sudden or intermittent engine stalling, it’s important to inspect the switch and fuse associated with the ignition system. A blown fuse or damaged switch can easily cut off power to critical components, causing engine failure. Replace any faulty components and double-check the fuse rating to ensure compatibility with the system’s specifications.
Lastly, ensure the timing of the system is properly configured. Incorrect settings or accidental changes during installation can result in an engine that runs poorly or doesn’t start at all. Use a timing light to check that the spark is firing at the correct point in the engine’s cycle. Adjust the system as necessary to match the recommended factory specifications.
Step-by-Step Troubleshooting for Ignition System Electrical Issues
1. Check for Power Supply – Ensure that the ignition unit is receiving the necessary voltage. Use a multimeter to measure the voltage at the power input terminal. Voltage should be consistent and match the specifications in the manual. If there is no power, trace the connection back to the fuse box and verify all fuses are intact.
2. Inspect Ground Connections – A poor ground can prevent proper operation. Verify that the ground wire is securely attached to a clean metal surface on the engine or chassis. A loose or corroded ground can lead to erratic performance or complete failure of the system.
3. Test the Trigger Signal – The ignition unit requires a signal from the distributor or trigger coil to function. Use a test light or oscilloscope to verify that the signal is being sent. No signal may indicate a faulty sensor or broken wiring.
4. Check the Coil – The ignition coil is a common point of failure. Inspect the coil for visible damage or signs of wear. Use an ohmmeter to check the primary and secondary resistance, and compare the readings to the manufacturer’s specifications. If the coil is defective, replace it with a new one.
5. Verify the Distributor – Inspect the distributor cap for wear or cracks. Ensure the rotor is firmly attached and not worn out. Examine the distributor’s shaft for any signs of movement or damage that could lead to misfiring.
6. Test the Control Unit – If the control unit is malfunctioning, the ignition system will fail. Using a diagnostic tool, check the status of the control unit to see if it’s functioning correctly. A reset may be required, or the unit might need to be replaced if it’s not responding.
7. Examine the Ignition Switch – A faulty ignition switch can prevent the system from powering on. Check for continuity in the switch, and ensure that the switch is securely connected. Replace the switch if it shows signs of failure.
8. Inspect the High-Voltage Wires – Inspect the spark plug wires for cracks, burns, or damage. High-voltage leaks can cause misfires or weak sparks, affecting engine performance. If any wires are damaged, replace them with high-quality replacements.
9. Test the Spark Plugs – Remove each spark plug and inspect it for carbon buildup or damage. A fouled spark plug can cause poor performance or no start. Clean or replace plugs that appear worn or damaged.
10. Look for Interference – Ensure that there are no external electrical interferences that could be affecting the system, such as nearby wires that could be shorting or causing cross-talk. Re-route any wires if necessary to eliminate potential sources of interference.