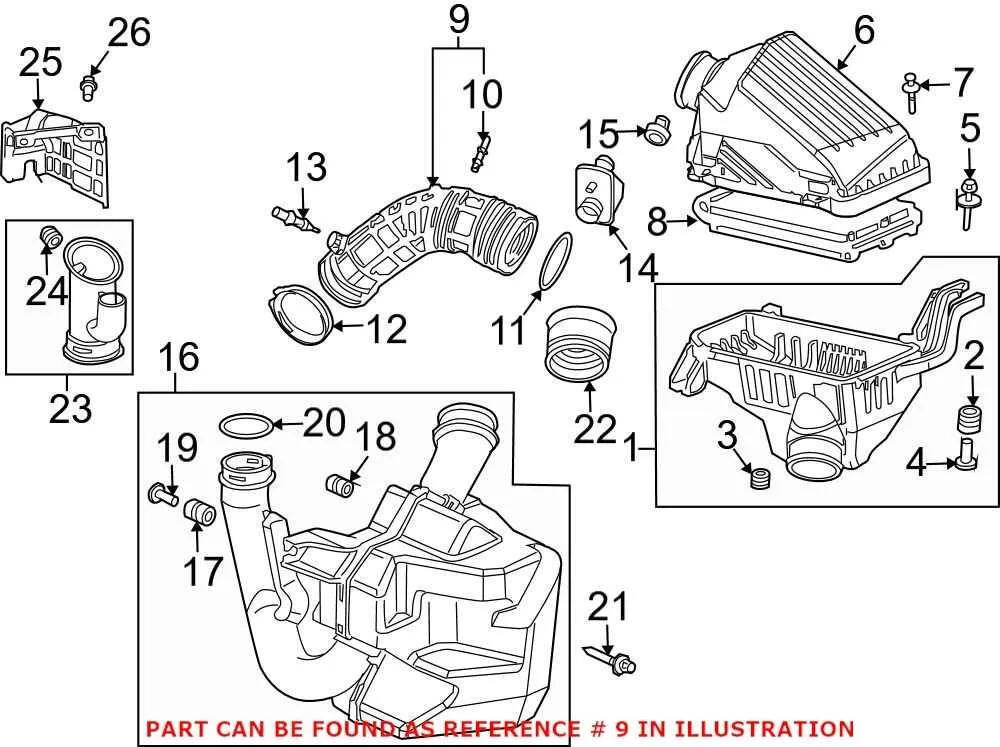
To ensure proper engine performance, it’s crucial to examine how the system channels air to the combustion chamber. A faulty connection in this setup can lead to poor fuel efficiency and engine misfire. Regular inspection of the components involved in this process is essential for maintaining optimal function. Be sure to check for any cracks, loose clamps, or signs of wear that could impede airflow.
When considering replacement parts, choose high-quality components that match the specifications of your engine. If the flexible conduit or the connecting tubes become damaged or degraded, replace them immediately to prevent unwanted air leaks. These leaks can result in improper air-fuel mixtures, leading to engine knocking and long-term damage.
Ensure that every connecting piece is sealed tightly and verify that all clamps are secure. A well-maintained ventilation pathway contributes to a smoother running engine, better fuel consumption, and reduced emissions. The path from the external environment to the engine is as vital as any other mechanical part and deserves regular attention for continued efficiency.
Understanding the Engine Duct Layout
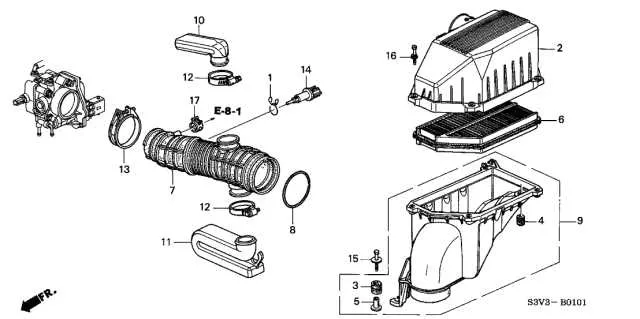
To ensure optimal engine performance, carefully inspect the pathway that channels the fuel mixture into the combustion chamber. Start by examining the flexible tube that connects the filter unit to the manifold, as any leak or damage here can reduce engine efficiency. Verify the integrity of the clamps and seals at both ends of the tube to prevent air entering the system in an uncontrolled manner.
Next, ensure that the system is free of blockages. Over time, debris can accumulate within the conduits, impeding airflow and causing the engine to run less efficiently. A thorough inspection using a flashlight and a small mirror can help locate hidden obstructions in the narrow sections of the path.
Also, inspect the routing of the conduit to confirm that it is securely attached to prevent unnecessary vibrations or movement. Loose connections can lead to air loss, which in turn may cause poor engine response or stalling.
Check the material for any signs of wear and tear. Aging conduits can crack or become brittle, leading to potential leaks. If cracks are found, immediate replacement is recommended to avoid performance degradation.
Understanding the Role of the Air Intake Hose in Engine Performance

Ensuring optimal airflow to the engine is essential for maximum performance. The component responsible for channeling filtered external gases into the combustion chambers plays a vital role in maintaining engine efficiency. Without a proper connection, the power output and fuel efficiency will decrease significantly.
The quality and condition of the conduit are critical. Cracks or leaks in the material will allow unfiltered elements to enter the system, potentially damaging internal parts. Regular inspection for signs of wear, especially around joints and seals, can prevent costly repairs.
Clogging due to debris or residue can also impede the passage of air, reducing engine responsiveness. Ensuring the path remains clear through regular cleaning or replacing the filter will keep the system running smoothly.
The construction material used affects the overall durability. Rubber components can degrade over time, but silicone or reinforced polymer variants offer longer-lasting reliability. Upgrading to high-quality replacements is a smart investment for those seeking to boost performance.
Temperature fluctuations can alter the density of the gases, affecting the engine’s fuel mixture. Using an insulated version of the part helps to mitigate this issue, ensuring that the air delivered remains at an optimal temperature for combustion.
Step-by-Step Guide to Reading and Interpreting an Airflow System Diagram
Start by identifying the components shown in the illustration. These typically include ducts, filters, and connections to the engine. Each element is represented by a specific symbol or line type. Look for labels and numbers, which indicate flow direction and part specifications.
Next, trace the lines that connect components. Solid lines usually represent primary pathways, while dashed lines indicate optional or secondary routes. Pay attention to intersections, which can show where multiple components interact or where a component might be added or replaced.
Focus on the filter element. It’s critical for maintaining proper function, so ensure its placement and connection are clear. Examine the airflow direction in relation to the engine and other components; this determines the system’s efficiency and performance.
Check the connection points, especially for clamps or fasteners. These are often indicated with symbols that specify the type of hardware needed or the torque required for securing components. Verify that the parts listed in the diagram match the physical items in your setup.
Finally, cross-reference any part numbers or manufacturer-specific details with the system’s service manual. This ensures that all components are compatible and that you’re following the correct installation or maintenance steps.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting Tips for Airflow System Components
Check for cracks or leaks in the flexible tubing. A simple visual inspection can reveal visible damage, but it’s also important to perform a pressure test to identify any hidden issues. Leaks can significantly reduce engine performance and fuel efficiency.
- Inspect for any obvious tears or wear along the length of the pipe.
- Use a smoke machine or aerosol leak detector to pinpoint hard-to-find leaks.
Ensure secure connections. If the fittings at either end are loose or improperly seated, the system will not operate efficiently. Tighten clamps or replace worn-out seals to restore the proper seal.
- Always tighten the clamps to the manufacturer’s recommended torque specification.
- Check rubber gaskets for wear and replace them if necessary.
Evaluate the routing of the system. Misalignment or incorrect positioning of the components can cause stress on the system, leading to premature failure. Ensure that the tubing follows the manufacturer’s recommended path and isn’t subjected to extreme temperatures or pressure.
- Keep the system away from hot engine components or sharp edges that could cause abrasion.
- Avoid tight bends that could restrict airflow or cause pressure build-up.
Monitor for clogging or blockages. Dust, debris, or even insects can accumulate in the system, restricting airflow and damaging the engine. Cleaning the system regularly helps maintain efficiency.
- Check the intake system periodically for dirt buildup, especially in areas that are hard to reach.
- Use compressed air or a vacuum to clear out any debris.
Replace damaged or outdated components. Over time, materials such as rubber or plastic degrade due to exposure to heat, oils, and other contaminants. Replace any parts showing signs of significant wear.
- Look for discoloration, brittleness, or cracks in the material.
- Consider replacing components with higher-quality or more durable alternatives if available.