For those looking to comprehend the arrangement of key components in the engine compartment of a 2008 Chevrolet sedan, focusing on the specific parts involved is essential. Knowing the precise positioning and functions of each element will aid in diagnostics, repairs, or modifications. The layout can be broken down into critical zones such as the fuel system, ignition system, and cooling elements. Understanding how these systems interact ensures optimal performance and prevents unnecessary wear.
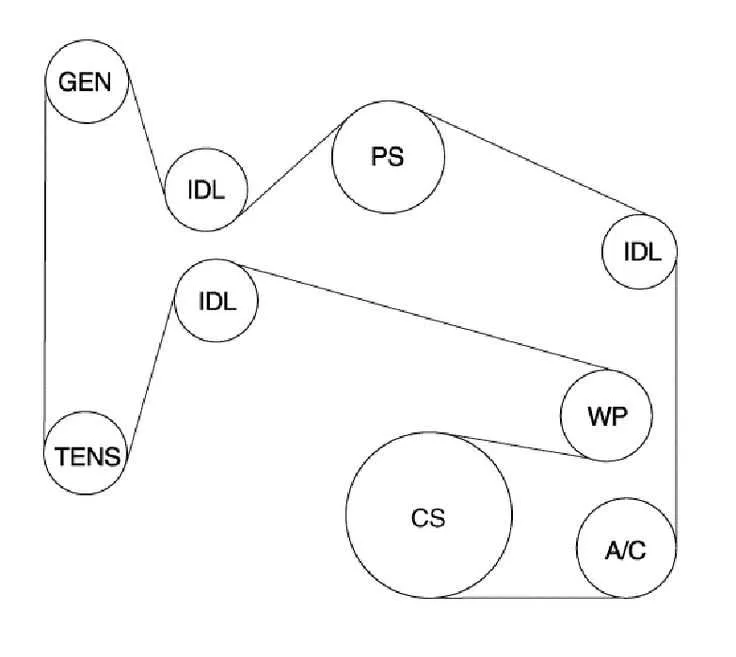
Pay attention to the placement of the alternator, starter motor, and battery, which are central to the vehicle’s electrical functionality. The timing belt and cylinder heads play a major role in the coordination of fuel and air flow, ensuring efficient combustion. Locating each of these components within the compartment will not only help when replacing parts but also when maintaining them for longevity.
Regular inspection of the radiator and its connections to prevent overheating is another practical recommendation. Additionally, understanding how the air intake manifold and exhaust system are positioned relative to one another will guide you in improving airflow efficiency, ultimately benefiting fuel consumption and engine life.
Powertrain Layout of 2008 Chevrolet Sedan
For accurate maintenance and repairs, it’s essential to understand the layout of key components within the vehicle’s propulsion system. Below are the primary parts and their connections in this model’s configuration:
- V6 configuration: A 3.5L V6 provides sufficient power for daily driving, delivering 211 horsepower at 5,800 RPM.
- Timing components: This model uses a chain-driven timing system, which reduces the need for regular replacement compared to belt-driven designs.
- Fuel system: Equipped with multi-port fuel injection, this ensures efficient combustion and helps maintain optimal fuel economy.
- Ignition system: The coil-on-plug setup minimizes misfires, improving fuel efficiency and reducing maintenance needs.
- Alternator location: Positioned near the front, it is easily accessible for routine checks and repairs.
- Cooling fan: The engine cooling fan is belt-driven and positioned directly behind the radiator for maximum cooling efficiency.
Proper maintenance of these components is crucial for the longevity of the powertrain and to avoid costly repairs. Regular checks of the timing chain, ignition coils, and fuel system will keep your vehicle running smoothly.
How to Identify the Main Components in the 2008 Chevy Impala Engine Diagram
Start by locating the powertrain at the center of the layout. The block, often identified by its rectangular shape, is where combustion occurs. On either side of it, you’ll find the cylinder heads, responsible for intake and exhaust processes.
Above the block, look for the intake manifold. This component is typically a wide, often curved structure that directs air and fuel into the combustion chambers. Adjacent to it is the throttle body, which regulates air flow into the intake system.
Next, identify the alternator, a crucial part of the electrical system. It sits near the front, connected to the crankshaft by a serpentine belt. The starter motor can be found close to the battery, often near the lower portion of the assembly.
On the side of the block, you’ll spot the timing chain or belt, which synchronizes the camshaft and crankshaft. This component ensures precise valve operation during each cycle. Above it, you’ll see the valve covers, which house the camshaft and valve train.
Next to the timing components is the exhaust manifold, usually found on the side opposite the intake manifold. It collects exhaust gases from the cylinders and directs them to the exhaust system.
Finally, look for the cooling system, with hoses running from the radiator to the water pump, which circulates coolant through the engine. The thermostat regulates the temperature by controlling coolant flow.
Understanding the Wiring Layout in the 2008 Chevy Impala Engine
For effective troubleshooting, first familiarize yourself with the fuse box locations and their associated power circuits. The primary relay panel is typically situated under the hood near the driver’s side. This is where the key electrical components like the ignition system, alternator, and fuel injectors are controlled. Make sure to inspect the ground connections around the chassis, especially near the battery, as poor grounding can lead to voltage instability and malfunctions.
The ignition system wiring should be checked for wear or cracks, particularly on the spark plugs and coil connectors. These connections are susceptible to high temperatures and can deteriorate over time. Use a multimeter to measure continuity in these circuits and ensure reliable spark delivery to the cylinders.
The fuel management wiring is interconnected with the mass airflow sensor and fuel injectors. A loose or corroded connection here can cause erratic fuel delivery, leading to engine performance issues. It’s recommended to clean and secure these connectors regularly, as fuel and debris can build up over time, obstructing the flow of power.
In addition to the powertrain circuits, pay close attention to the connections that regulate the transmission system. Many control modules for shifting are linked to the main electrical network, and a malfunction in this section can result in improper gear engagement or delayed shifting. If your vehicle is experiencing these issues, a close inspection of the transmission wiring harness is crucial.
Lastly, the cooling system relay wires and temperature sensor connections play an important role in maintaining engine temperature. Check these wires for damage and ensure proper insulation. Damaged or faulty cooling circuit wiring can trigger overheating, affecting engine longevity.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting Methods
Misfiring often results from faulty spark plugs or ignition coils. Check the spark plug connections and ensure the coils are properly seated. If the problem persists, inspect the fuel injectors for blockages or leaks, as fuel flow issues can also cause misfires.
Overheating can stem from a variety of causes, such as a malfunctioning thermostat or a leak in the cooling system. To identify the source, monitor the temperature gauge for unusual spikes. Ensure the coolant level is adequate, and inspect the radiator for signs of damage or corrosion.
Low Oil Pressure may indicate a worn-out oil pump or a clogged oil filter. Begin troubleshooting by checking the oil level and the condition of the oil. If the oil appears dirty or gritty, a full change might be necessary. Inspect the oil pump for proper functioning and replace it if needed.
No Start issues can often be traced to a faulty fuel pump, battery, or starter. If the battery is fully charged and the starter motor does not engage, check the fuel pump relay and the fuse. If both are functional, the fuel pump itself may need to be replaced.
Unusual Noises like knocking or pinging typically signal issues with the timing or fuel mixture. Review the ignition timing and fuel quality. If the issue is persistent, consult the wiring and components of the timing system to ensure proper alignment.
Use a systematic approach to identify the issue–start with basic checks like fluid levels and connections, then proceed to more complex systems like the timing or fuel delivery mechanisms. Always refer to the specific component layout for accurate troubleshooting steps.