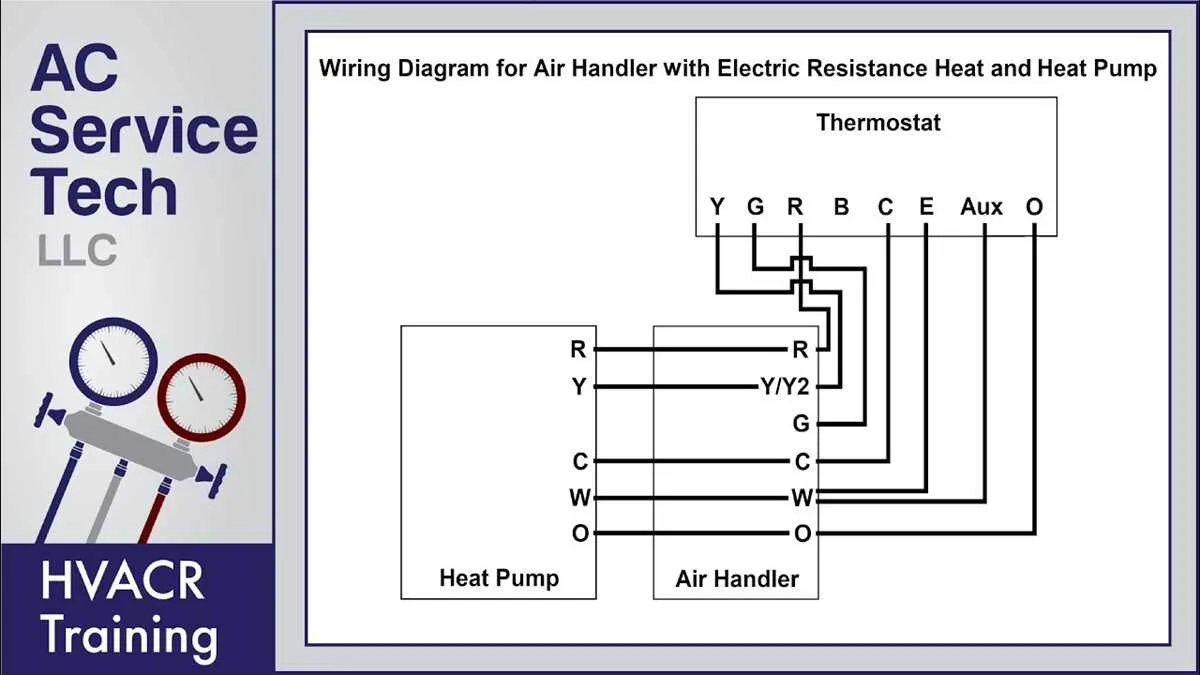
To properly troubleshoot or maintain an HVAC system, it’s crucial to have a clear understanding of the electrical layouts that govern its operation. If you’re facing difficulties with your unit’s electrical system, referring to the correct wiring layout can help pinpoint issues, whether it’s a faulty connection, a malfunctioning component, or an electrical short. The first step is identifying the system’s components, including the compressor, reversing valve, and thermostat, to ensure they are wired correctly and functioning as intended.
Focus on understanding the connections between the different components. Typically, these systems have specific terminal points for the connections to ensure that power flows correctly through the various stages. Pay close attention to the color-coding of wires, as this will guide you in identifying whether you’re dealing with the correct voltage levels and phases. In some cases, improper wiring can lead to equipment damage or operational inefficiencies.
Double-check the control board layout, which acts as the heart of the system’s electrical functions. Most issues arise from incorrect wire placements or faulty connections at the control panel. Make sure each wire is connected to the correct terminal as indicated by the manufacturer’s instructions. If a wire is loose or incorrectly positioned, it can prevent your system from cycling properly or cause power surges that may damage sensitive components.
Ensure that all components are securely grounded and that there are no exposed wires. Also, if you notice any discoloration or burn marks around the connectors, it’s a clear sign that excessive heat has been generated in that area, possibly due to an overload or faulty component. It’s vital to address these issues immediately to avoid further damage.
Understanding Electrical Schematics for Temperature Control Units
When setting up or troubleshooting a temperature control system, it’s crucial to follow the specific electrical connections indicated by the manufacturer. These schematics provide clear instructions on how to wire components such as the compressor, thermostat, and fans. Here’s what to consider:
- Ensure proper power supply connections are made according to the system’s voltage rating.
- Check the sequence of terminals for controlling the compressor and reversing valve, which dictates the unit’s operation mode.
- Make sure all ground connections are securely in place to prevent electrical hazards.
The control board is typically the central hub of operations. Pay attention to the pinouts for the sensors and actuators. Incorrect wiring can lead to improper function, such as malfunctioning fans or inconsistent temperature regulation.
Verify the connections for the outdoor and indoor components to ensure they are properly interlinked. The thermostat should be connected to the control panel, and the reversing valve must be wired according to the heating or cooling cycle requirement.
- Double-check the connection of the capacitor, which helps maintain the operational efficiency of the compressor motor.
- Inspect the fuse and breaker connections for overload protection and ensure they are rated correctly for the specific model.
Refer to the specific schematic for the exact placement of each wire. Improper connections can lead to short circuits, inefficient operation, or even permanent damage to the system. Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines closely.
Understanding the Common Electrical Connections in Rheem Heat Pumps
Ensure proper connection of the transformer to the control board to supply correct low-voltage power to the system. The primary circuit typically uses a 24V supply, and proper connection is crucial for efficient operation.
The defrost control board often requires a specific wiring configuration for accurate temperature sensing. Make sure the sensor is connected securely to the control circuit. A loose or damaged connection here can lead to incorrect defrost cycles, affecting system efficiency.
The contactors should be installed with careful attention to correct placement of line voltage and low-voltage connections. The contactor’s coil should receive the proper 24V signal from the control board to activate the system’s main components.
For systems with auxiliary heat elements, ensure they are connected to the corresponding relay and control board. Miswiring of these components can lead to overheating or underperformance during demanding conditions.
Ensure fuses and breakers are correctly installed and rated for your system. A mismatch here can cause system malfunctions or damage sensitive components.
Finally, check the communication lines between the main control board and other components. Proper connections here are essential for system diagnostics and overall functionality.
How to Troubleshoot Electrical Issues Using Diagrams
Start by identifying the power source and confirming that the system is receiving the correct voltage. Use a multimeter to check if the voltage matches the specifications outlined in the system’s technical manual.
Next, verify the connections to each component by inspecting the terminals. Loose or corroded connections can cause intermittent power loss or complete failure. Tighten any loose connections and clean off any oxidation that may impede conductivity.
If the unit is not turning on, check the control board for any visible signs of damage, such as burnt areas or blown fuses. Ensure that all connections to the board are secure and free from debris. If necessary, replace any damaged components according to the schematic provided.
Examine the relay switches and capacitors for proper function. A faulty relay can prevent signals from reaching critical components. A malfunctioning capacitor may cause the system to lose power or fail to start. Consult the diagram to match each component’s specs and replace any faulty parts.
Test the continuity of each wire in the system. A broken or damaged wire can disrupt the electrical flow. Use the diagram to trace the wire path and determine where continuity is lost, then repair or replace the affected section.
For more advanced troubleshooting, check the system’s sensors. An incorrect reading from a temperature or pressure sensor can cause the unit to shut down. Cross-reference the sensor readings with the expected values in the system’s documentation.
Finally, after performing all checks and repairs, power the system back on and test its operation. Ensure that all components are running smoothly and monitor the system for any signs of recurring issues.
Step-by-Step Guide to Installing a Heat Transfer System Using Electrical Schematics
Start by ensuring that the electrical power is turned off at the main breaker panel to avoid any hazards during installation.
Next, connect the main unit’s terminal block to the appropriate power source, following the color-coded guidelines for each wire. The common connections typically include L1 for live, L2 for neutral, and ground for safety. Double-check the wire gauge and ratings to match the system’s requirements.
Secure the control wires to the designated terminals on the interface board. These wires control the switching mechanisms for the internal fans, compressors, and other components. Carefully refer to the schematic to place each wire in its correct slot to ensure proper function.
Once the internal wiring is connected, install the communication link between the outdoor and indoor sections. These connections are vital for the system’s operational coordination. Be sure to match the communication cables to their designated ports as outlined in the electrical map.
After ensuring all connections are made securely, connect the thermostat wires. The wire typically runs from the unit to the control board, where it regulates temperature settings and adjusts the system’s performance accordingly. Again, verify the terminal points based on the provided electrical layout.
Before powering up, check that all terminals are firmly secured and that there is no exposed wire. It’s crucial to ensure no shorts or improper connections, which could damage the unit or cause operational failure.
Power on the system and test each function, starting with the fan and gradually moving to the compressor and heating functions. Monitor the system closely for any signs of malfunction. If everything works as expected, the installation is complete.
Final Check: Double-check all connections and confirm that the system is properly grounded to ensure safe and efficient operation. If any issues arise, refer to the specific electrical maps to troubleshoot the installation.