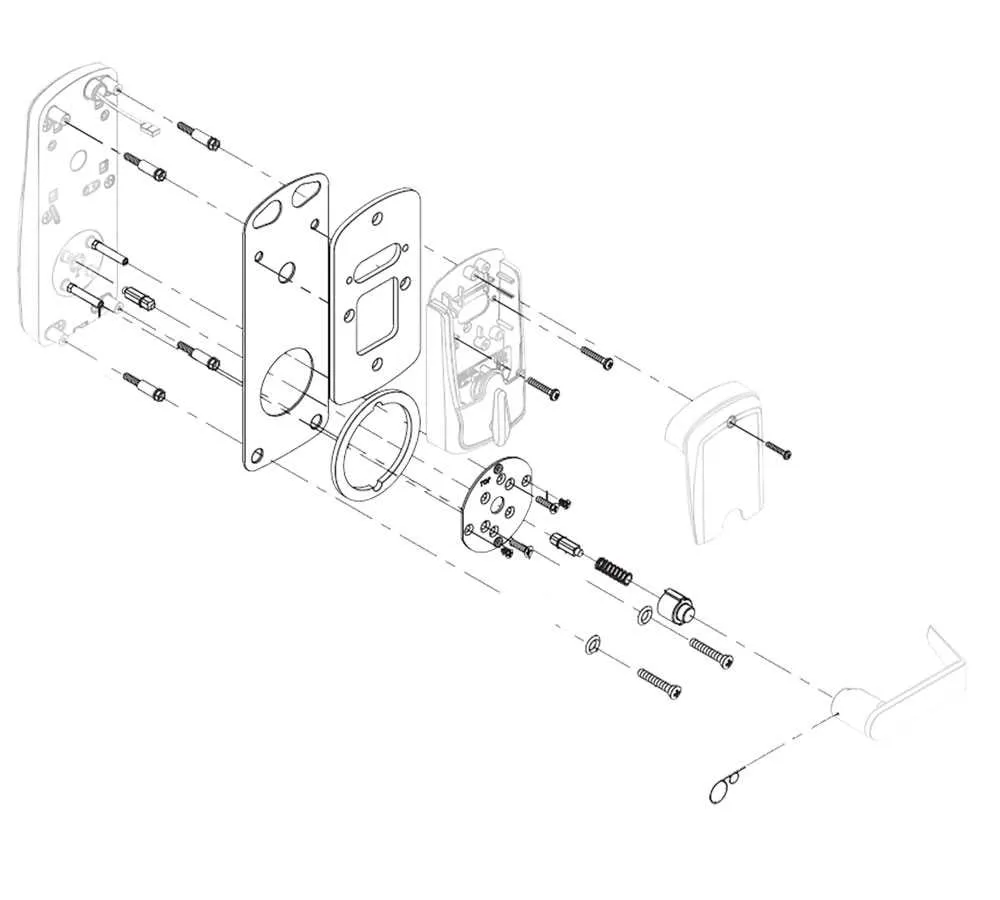
To successfully repair or replace the key elements of your locking mechanism, refer to a detailed breakdown of each individual component. This ensures accurate identification and understanding of all the necessary parts required for maintenance or upgrades.
Start by examining the locking unit’s interior workings. Commonly, this will involve inspecting the latch, spindle, and strike plate. These are the components that ensure proper engagement and alignment when the door is closed. Check for any signs of wear, corrosion, or misalignment that may prevent smooth operation.
Next, review the external mechanisms. The handle or knob, for example, is often one of the most commonly replaced parts due to regular use. It’s crucial to choose a replacement that fits securely within the housing, ensuring long-term functionality.
Ensure all screws and fasteners are properly tightened to prevent loose connections, which can lead to malfunction. Over time, these connections can degrade, causing the entire unit to become unstable or unresponsive.
Finally, always follow the manufacturer’s guide for proper assembly. Using an accurate representation of the lock’s internal and external components helps in reassembling the unit correctly, ensuring optimal security and operation.
Component Breakdown for Lockset Assembly

When assembling or servicing your lockset, refer to the following detailed breakdown of key components. Ensuring each part is correctly identified and in place is crucial for smooth operation.
- Exterior Handle: The outermost part that serves as the main interface for operation. It often includes a keyhole for traditional locking mechanisms.
- Interior Knob: Located inside, this component allows the user to operate the lock from within. Make sure it is aligned with the spindle correctly.
- Latch Bolt: This component slides into place to secure the door. Verify that it moves freely within the mechanism to prevent sticking or jamming.
- Strike Plate: The metal plate installed on the door frame to receive the latch. It must be securely fastened and aligned with the latch for proper functionality.
- Spindle: The rod that connects the two handles, allowing them to rotate in sync. Ensure the spindle is positioned securely to avoid loosening.
- Thumbturn: Found on the interior side, this part controls the locking mechanism. Regular lubrication will prevent it from sticking or becoming hard to turn.
Check that all these parts are securely fitted and functioning before final installation. A misaligned component may affect the entire lockset’s performance, leading to malfunction or increased wear.
Understanding the Key Components of a Digital Lock

The main elements of a modern digital entry system include the lock body, the latch mechanism, the cylinder, and the keypad. These components work together to ensure secure access control and proper functioning.
The lock body serves as the foundation for all other parts. It houses the locking mechanism and integrates with the door, securing it when the system is engaged. For smooth operation, ensure the body is aligned properly with the door frame.
The latch mechanism is crucial for engaging and disengaging the lock. It operates through the turning of the knob or pressing the appropriate button on the interface. Any malfunction in this part can result in the failure to lock or unlock the door properly, which is why it’s essential to maintain its alignment and smoothness.
The cylinder is the heart of the locking system, where the key or code is inputted to gain access. The mechanism inside the cylinder interacts with the locking elements, ensuring the system is activated when the correct input is provided. This part is often sensitive to wear and tear, so regular cleaning and lubrication are recommended.
The keypad or entry interface, which may include a touch screen or physical buttons, allows the user to enter their access credentials. The quality of this part can affect how quickly and efficiently access is granted. Ensure that the keypad is free of obstructions, and check its connections periodically to avoid performance issues.
How to Identify and Replace Faulty Components
To pinpoint a malfunctioning element in your locking mechanism, begin by checking the keyhole and internal turning mechanism for resistance or irregular movement. If the latch does not retract smoothly or the locking pin doesn’t engage properly, it’s likely that the internal springs or the locking mechanism itself is worn out.
Start by disassembling the lock, ensuring all screws are removed carefully. Examine the inner components for visible wear, corrosion, or misalignment. Common issues include bent bolts, stripped screws, or damaged springs. Once the faulty part is identified, order a replacement based on model compatibility.
When replacing a worn-out spring or latch, ensure the new component matches the original in size and function. For springs, verify the tension and size to avoid malfunctioning. Install the new part, reassemble the lock, and test the function by turning the handle and checking the lock’s response when engaged. If everything works smoothly, the issue has been resolved.
Always keep extra screws, springs, and internal gears on hand to avoid delays in repair. Regular inspection and maintenance of the locking system can prevent frequent breakdowns and prolong the device’s lifespan.
Steps to Assemble the Lock Mechanism Correctly
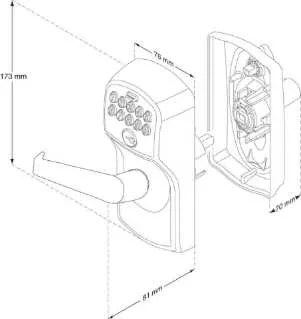
Begin by ensuring that all essential components, including the exterior and interior parts of the lock, are present. Identify the correct orientation of the locking mechanism, as improper alignment can lead to malfunction.
1. Attach the Exterior Handle – Position the exterior handle in alignment with the latch assembly. Secure it with the provided screws, ensuring the mechanism is firmly connected. Be sure not to overtighten, as this could strip the threads.
2. Install the Interior Assembly – Align the interior unit with the exterior handle. Ensure the bolt mechanism slides into place without obstruction. The internal locking mechanism should engage seamlessly when inserted.
3. Secure the Strike Plate – Attach the strike plate to the doorframe, making sure it is aligned with the bolt’s path. This step is crucial to ensure smooth locking and unlocking actions. Use screws to fasten the plate, checking that it remains flush with the doorframe.
4. Test the Locking Functionality – Before final installation, test the locking mechanism by turning the knob or handle. Ensure the bolt extends and retracts without resistance. This step guarantees that the lock is assembled correctly and functions as intended.
5. Final Tightening and Check – After confirming functionality, tighten all screws and bolts securely. Inspect for any looseness and verify that the interior and exterior components are properly seated. Any loose parts may compromise the lock’s performance over time.