
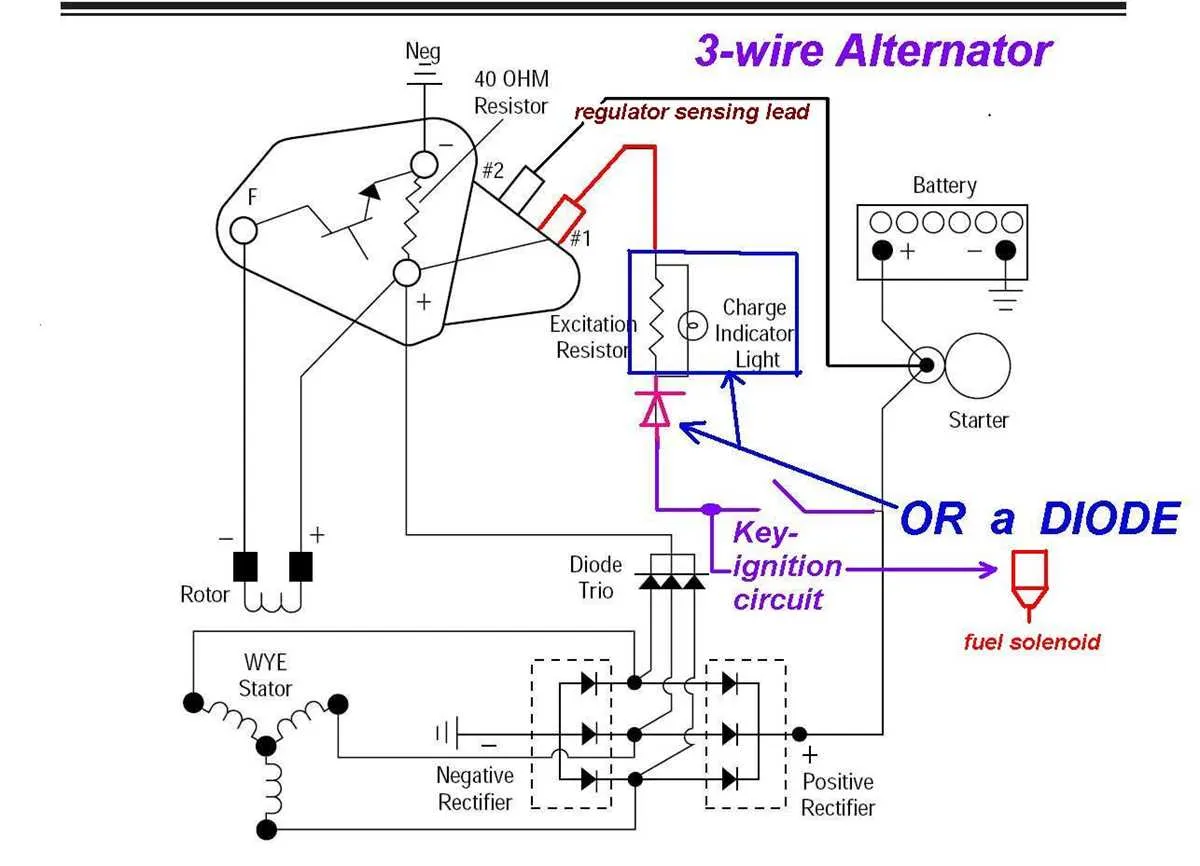
For an efficient setup of your charging system, ensure a proper connection of the main power output to the vehicle’s electrical network. The main component responsible for energy generation should be correctly connected to both the battery and the control unit to maintain consistent power flow.
Focus on grounding: A solid ground connection is crucial to avoid electrical surges and system malfunctions. The ground connection should be secure, free from corrosion, and linked directly to the vehicle’s chassis or a designated ground point. Use the recommended gauge of wire for this purpose.
Correct voltage regulator connection: The voltage regulator should be connected to the output terminal of the generator, ensuring that the charging voltage remains within the acceptable range. Inconsistent voltage regulation can lead to overcharging or undercharging the battery, potentially damaging both the battery and other components.
Consult the manufacturer’s specifications: Always verify the exact specifications for your generator model. Different systems may require specific methods of installation, especially in cases where advanced control mechanisms or additional sensors are involved.
Wiring Setup for One-Wire Charging System
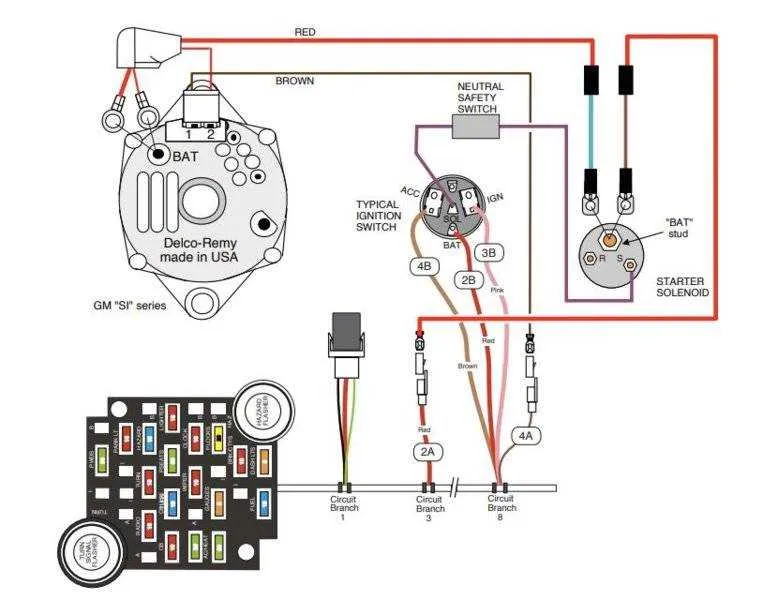
To properly connect a one-wire charging system, start by ensuring the output terminal on the generator is linked directly to the battery’s positive terminal. This setup simplifies the process by removing the need for multiple connections. Make sure to use a wire of sufficient gauge to handle the current load without excessive resistance.
The regulator is integrated into the system, eliminating the need for an external component. Once connected, the charging unit will begin producing power immediately after the engine starts. Be cautious when installing, as improper grounding can cause the unit to malfunction or fail to charge the battery efficiently.
For optimum performance, the unit’s field terminal typically does not require connection. This is because the internal regulator controls the voltage. If your setup includes a dashboard voltage gauge, it should also be wired to the positive terminal to monitor performance during operation.
A key recommendation is to ensure a clean, secure ground connection between the generator and the engine block to maintain proper functionality. Any loose or poor grounding can lead to erratic behavior or undercharging, reducing the lifespan of your battery.
Understanding the Function of the One-Wire Charging System
The one-wire system simplifies the charging process by using a single connection for power and regulation. This setup eliminates the need for separate field connections and external voltage regulators, making installation faster and reducing potential points of failure.
In operation, the generator produces electricity as the engine runs, supplying power to the vehicle’s electrical components. The current flow through the main lead triggers the internal regulator, which adjusts the output voltage based on load demand. The key advantage of this configuration is its ability to self-excite, meaning it can begin generating electricity as soon as the engine starts, without any external input or control signals.
For efficient functioning, it’s crucial to ensure that the connection is securely grounded and the battery has sufficient charge to allow for initial excitation. A reliable connection also minimizes voltage loss, ensuring proper performance under varying loads.
One of the primary benefits of this design is reduced complexity in the electrical system. With fewer components, troubleshooting becomes easier, and the overall system is more resilient against wiring issues. However, a properly installed and maintained unit is essential for optimal operation.
How to Connect the Single-Wire Generator to the Electrical System
Start by connecting the charging unit directly to the vehicle’s electrical circuit. This ensures efficient power generation and battery charging. Follow these steps for optimal integration:
- Connect the positive output terminal: Attach the unit’s positive terminal to the battery’s positive post. Use a properly sized cable for secure and efficient power transfer.
- Ground the system: Establish a solid connection between the unit’s negative terminal and the engine block or chassis. This helps to prevent electrical faults and ensures proper functionality.
- Install a voltage regulator: Ensure that the generator includes an internal voltage regulator or install an external one if necessary. This keeps the voltage within safe limits and prevents overcharging the battery.
- Check the ignition switch connection: Connect the ignition switch to the unit to activate it once the engine starts. This activates the charging process, keeping the battery replenished during operation.
- Monitor wire size and insulation: Choose cables that can handle the expected current load. Use heat-resistant insulation to prevent overheating and potential failure.
After completing the connections, perform a voltage check with a multimeter to ensure that the system operates correctly. The voltage should increase once the engine starts, indicating proper function.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting Tips for Single-Connection Charging Systems

Low Output Voltage: If the system isn’t generating sufficient voltage, check the connection to the battery and ensure that it is clean and free of corrosion. Poor contact can significantly reduce the charging efficiency. Also, measure the output at the terminal using a multimeter to confirm whether the voltage is within the expected range of 13.5 to 14.5 volts when the engine is running.
Insufficient Charging or No Charging: In many cases, a lack of output is due to a faulty regulator. Inspect the voltage regulator for any visible damage or wear. Additionally, inspect the brushes for wear or damage, as these components are essential for maintaining a stable electrical connection.
Intermittent Function: If the system charges intermittently, the root cause may be loose or damaged connections. Check the output terminal, ground, and all electrical connections for tightness. Vibration or movement from the engine could cause weak connections to break contact intermittently.
Overcharging: If the battery is being overcharged (exceeding 15 volts), it is likely due to a faulty voltage regulator or a malfunction in the field coil. Overcharging can lead to damage to the battery, so replacing the faulty regulator or coil is necessary to prevent further damage.
Charging Fluctuations: If the charging voltage fluctuates, consider checking for grounding issues. A poor ground connection can cause the system to fluctuate under load. Ensure the ground point is clean and well-secured, as this is a common source of voltage instability.
No Output After Installation: After installation, if there’s no output, double-check the system’s connections and confirm that the system is properly grounded. Incorrect or incomplete grounding is one of the most common issues after installation. A quick ground continuity test using a multimeter can help confirm if this is the issue.
Performance Drop Over Time: A gradual performance drop may be related to the aging of internal components, such as the regulator or the diodes in the rectifier assembly. If the output begins to degrade, consider replacing these parts to restore optimal functionality.