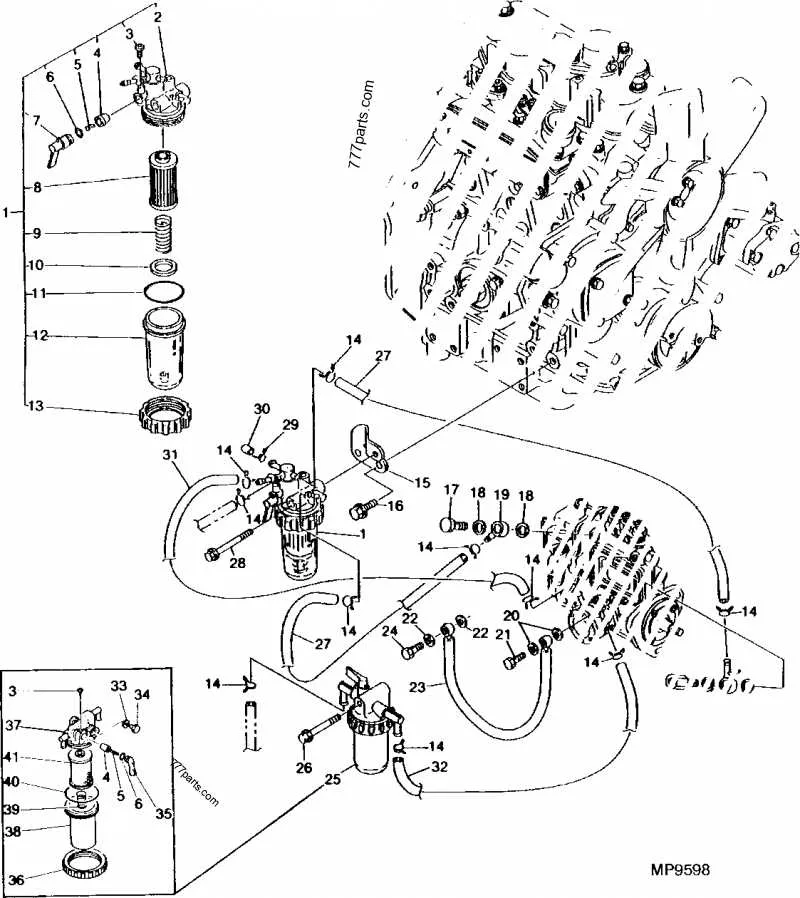
For efficient engine operation, it is crucial to understand the arrangement of fluid pathways within the tractor’s powertrain. This involves closely inspecting the routing of components that transport vital liquids to and from key systems. Proper maintenance of these elements ensures optimal performance and prevents leaks or blockages.
Ensure that all connecting hoses and components are securely fastened to avoid any potential disconnections that could result in malfunctions. If any part appears worn or damaged, replace it promptly to avoid compromising the tractor’s power system. Pay special attention to areas that experience constant friction or exposure to extreme temperatures.
Regularly check for any signs of leakage at connection points. If liquid buildup is noticed around any junctions, it may indicate that seals have degraded or that parts are misaligned. A precise examination of these regions can help identify potential issues early, saving on costly repairs in the future.
Replacing damaged components is a straightforward process if done systematically. Always refer to the manufacturer’s specifications when selecting replacement parts to ensure compatibility. Consistency and proper alignment are key to maintaining the integrity of the entire system.
Detailed System Routing for Fuel Lines on Model 7775
For efficient maintenance, it’s crucial to understand the exact configuration of the system responsible for transporting fuel through the engine. Follow these instructions carefully to ensure smooth operation and prevent common issues like clogging or leaks.
- Start by locating the primary connector points. These are usually situated near the engine block and the fuel tank inlet. Ensure both ends are free from corrosion and tight connections.
- Examine the routing path; the path should be clear of any wear points or areas exposed to high heat. It’s recommended to install additional protective covers if needed to safeguard the tubing.
- Check for any points where the tubing may have kinks or sharp bends. These can restrict the flow of fuel and cause pressure imbalances.
- Inspect the securing clamps along the tubing. If any are loose or deteriorated, replace them to maintain system integrity.
- Ensure that all connections are sealed with O-rings or gaskets to prevent leakage, especially at the junctions where the pipes meet the fuel injectors or filters.
- If replacing any sections of tubing, use only high-quality material that is rated for the temperature and pressure conditions specific to this engine model.
Performing these checks will help you maintain optimal performance and prevent costly repairs due to fuel delivery issues.
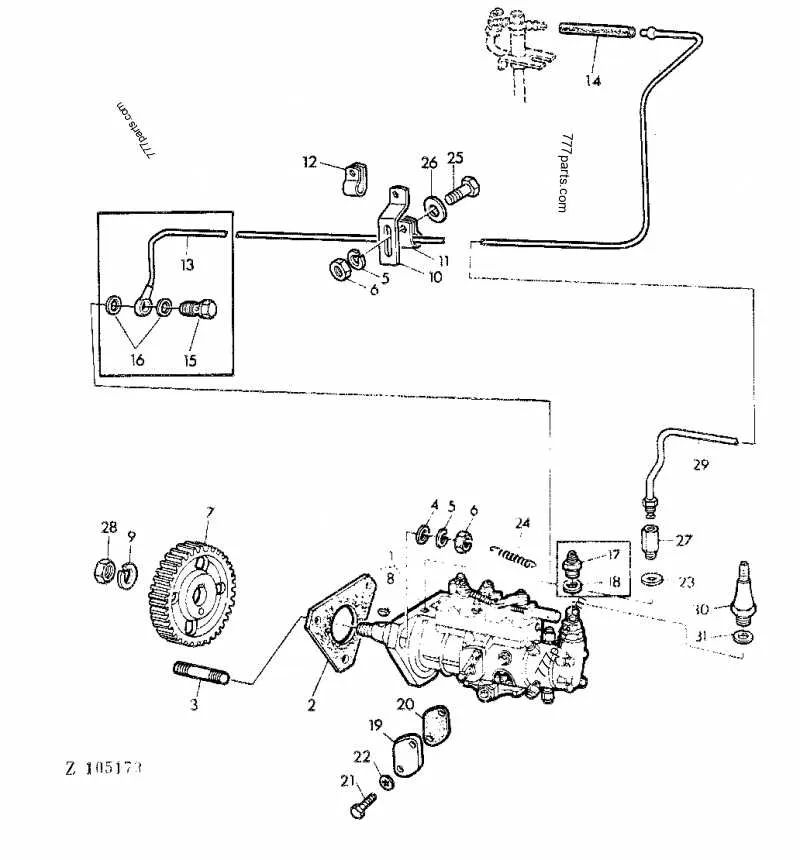
Understanding the Fuel System Components of the Tractor
To ensure optimal performance and prevent malfunctions, regularly inspect the system responsible for transporting liquid to the engine. Start by checking the hoses and connectors for any cracks or signs of wear. Replace any component that appears damaged to avoid leaks or fuel loss during operation.
Pay particular attention to the filter, which helps to prevent debris from entering the engine. A clogged filter can restrict flow, leading to decreased efficiency or potential engine damage. Clean or replace the filter as needed based on the manufacturer’s maintenance schedule.
The pump, which moves the liquid through the system, should also be regularly checked for any signs of malfunction, such as inconsistent pressure. Any loss of pressure can lead to engine performance issues, so it’s important to address pump problems promptly.
Ensure all clamps and fasteners are tightly secured to avoid any risk of system loosening during operation, which could lead to spillage. If the system uses any sensors, verify their function periodically to maintain accurate pressure readings and flow control.
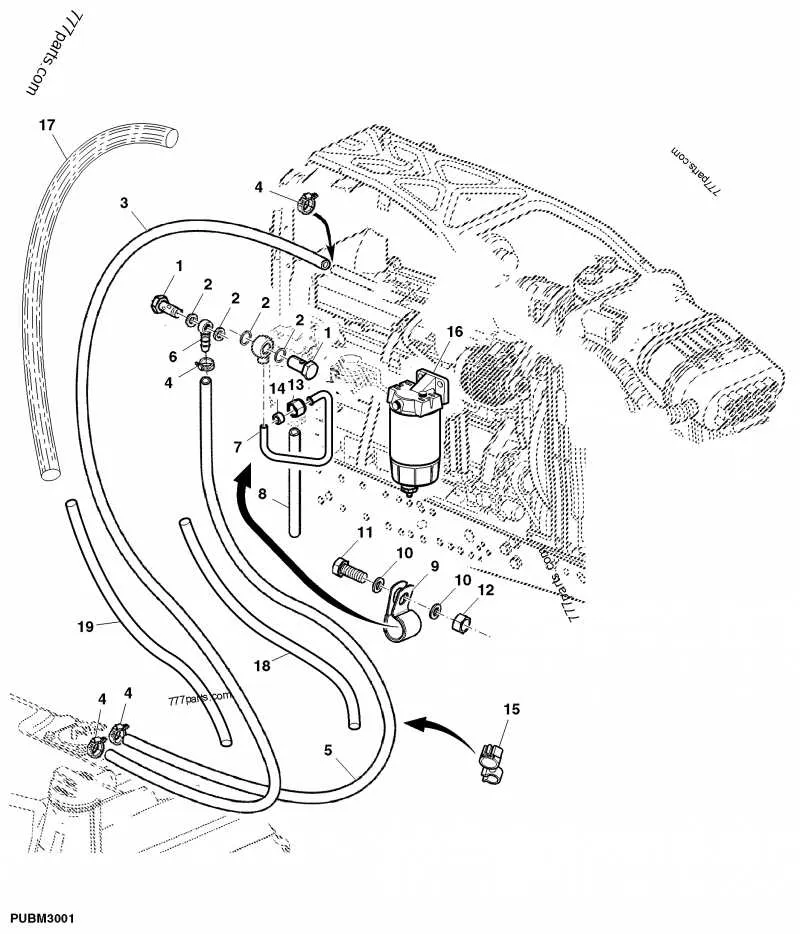
Step-by-Step Process for Inspecting Fuel System Connections
1. Start with Disconnecting the Battery: Ensure that the power is completely off by disconnecting the battery before starting any work on the engine or powertrain system. This will minimize the risk of electrical hazards or accidental activation of components.
2. Locate and Inspect the Hoses: Identify the key hoses that transport the vital liquids from the tank to the engine. Check for signs of cracks, abrasions, or any bulges in the material. If any wear or damage is detected, replace immediately to prevent leaks.
3. Check for Leaks: After identifying the hoses, visually inspect all connections for any signs of leakage. Pay close attention to where the hoses meet the connectors or fittings. If there’s any indication of drips or residue, tighten the fittings or replace seals as necessary.
4. Examine the Clips and Fasteners: Ensure all clips and fasteners are securely holding the hoses in place. Loose fasteners can lead to slipping or unintentional disconnections, which might cause system failures.
5. Test the Flow Pressure: Use a pressure gauge to test the system’s pressure. Inadequate pressure can be a sign of blockages or leaks somewhere within the transfer system. If the pressure is too low, identify any clogs or constrictions that may need addressing.
6. Inspect the Fuel Filter: It’s crucial to verify that the filtration system is clean and functional. If the filter appears dirty or clogged, replace it to ensure proper flow and efficiency of the engine.
7. Final Check and Reassembly: Once all components have been inspected, reassemble the system carefully. Ensure that everything is tightened to the manufacturer’s specifications. Perform a final visual inspection for any missed connections or potential points of failure.
Common Issues with Fuel System Components and Troubleshooting Tips
If the system is not delivering the proper amount of pressure, start by inspecting the connections for blockages. A restricted fuel pathway can cause poor engine performance or stalling. Check for cracked hoses, loose connections, or clogged filters. Tightening or replacing these parts can resolve most pressure-related issues.
Another common issue involves air pockets within the system, which can disrupt fuel flow and lead to starting problems. To fix this, bleed the system thoroughly to eliminate any trapped air, ensuring consistent pressure. If the issue persists, consider examining the pump for potential malfunctions that could affect pressure regulation.
Leaks around connectors or components are a frequent problem and should be addressed immediately. Leaking fuel poses a fire hazard and reduces system efficiency. Check all gaskets and seals to ensure they are intact. Replacing worn seals or tightening loose connections can prevent fuel loss.
Ensure the filter is not obstructed by debris, which can limit fuel flow and impair engine performance. Replace filters on a regular schedule to maintain optimal operation. Additionally, verify that the fuel tank is not contaminated with water or debris, as this can damage the entire system. Flushing the tank and cleaning all filters should eliminate this issue.
Fuel delivery problems could also arise from faulty injectors. Inspect the injectors for wear or clogging. Cleaning or replacing malfunctioning injectors ensures the engine receives the correct amount of fuel for optimal combustion.